

- Digital forensics techniques windows linux mac os for mac#
- Digital forensics techniques windows linux mac os mac os x#
These dimensions can range from very large to very small. A document may have multiple thumbnails, each one having different dimensions.Quick Look thumbnails are tracked using a SQLite database, which stores a last-hit-date and hit-count for each one.Quick Look thumbnails are not only stored for documents on internal disks they are also stored for documents located on removable disks, including those that have been encrypted.

Digital forensics techniques windows linux mac os for mac#
Microsoft, for instance, package its own Quick Look generators together with the Microsoft Office for Mac suite of applications.
Digital forensics techniques windows linux mac os mac os x#
The Quick Look function within Mac OS X caches thumbnail images so as to avoid unnecessary, repetitive processing, thereby increasing performance.Įxamination of a Mac OS X user’s Quick Look thumbnail cache can provide evidence of guilty knowledge it may also reveal the presence of documents that would otherwise be inaccessible or go unnoticed by the examiner. It enables applications such as Spotlight (the Mac OS X search application) and Finder (the Mac OS X equivalent of the Windows Explorer program) to display thumbnail images and full-size previews of supported documents. Quick Look is a technology that was introduced by Apple in Mac OS 10.5. With each release of EnCase, there are fewer techniques that remain best-suited or unique to a native OS X toolset. If you haven’t used EnCase for OS X investigations, you may not be aware EnCase has been continuously adding support for investigation of OS X systems, including the comprehensive support for HFS+ extended attributes, Plist parsing, an automated OS X artifact processing module, as well as most recently, native support for decryption of OS X keychains. However, many investigators lack access to a Mac for forensic investigation. To preface this post, many artifacts created in OS X are most easily reviewed and understood on a Mac natively. In this post, we’ll explore how this particular artifact can be exposed and understood in your next OS X investigation. In OS X, there is a relatively under-exploited source of thumbnails generated from Quick Look technology. It helps when determining the investigative approach.Thumbnail images can be extracted from a variety of sources in a given piece of evidence under investigation (e.g., cached browser images, thumbs.db files, embedded JPEGs, etc.).
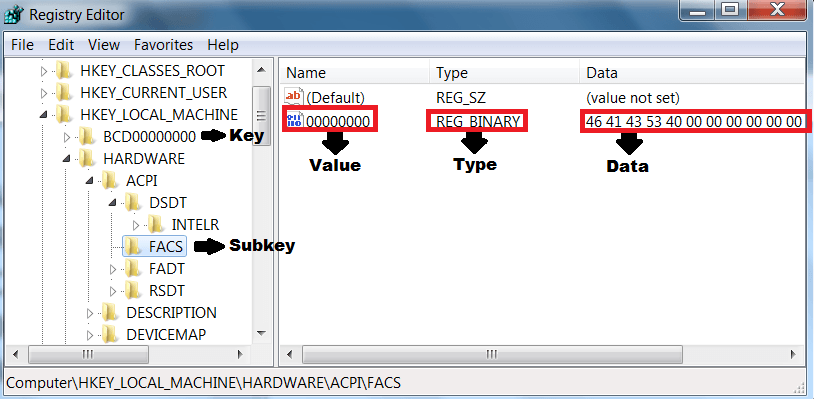
As a result, knowing the type of Operating System one is dealing with is a critical part in forensics investigation. This helps in examination of physical hard drives. Thirdly, both operating systems have hierarchal file management systems (Bajgoric?, 2009). Secondly, both operating systems have permissions for files, which are important during forensics investigations (Bajgoric?, 2009). The first similarity of windows and Linux forensics investigations is that same tools can be used in both cases. For Linux, one runs IS I common on specific file or directory, while in windows one finds this in the security tab by opening the registry artifacts. Thirdly, the criteria used for viewing file permissions differ in Linux and Windows. This is possible because Linux uses a virtual file system (VFS) to merge all files (Liu, 2011). Secondly, during Linux forensics, investigators can access all the files in a single OS, while this is not the case with MicrosoftÆs windows. The root, which is the only administrative account in Linux, has all the information about system control (Liu, 2011). The biggest contrast between windows and Linux forensics is that with windows one will have to look for data from various administrative accounts, while for Linux, investigations target one administrative account (Liu, 2011). "Windows and Linux Forensics Investigations"


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
